International Monitoring System (IMS)
The Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (the CTBTO Preparatory Commission) sets up the International Monitoring System (IMS) to monitor nuclear weapon test explosions around the world and aims to complete a verification regime to provide all signatories with related information by 2007. 337 monitoring stations, which use 4 monitoring methods, monitor seismic, hydroacoustic and infrasound vibrations and radionuclide respectively, and can detect every nuclear test explosion over the magnitude of 1 kiloton on the globe.
A large image in a new window is opened on click. The IMS comprises those monitoring stations and the line of communication and is supported by the International Data Center (IDC) in Vienna. The signatories exchange the data internationally and have access authority to all data transmitted to the IDC.
In accordance with the CTBT, there are 10 monitoring facilities in Japan.
| Seismic Monitoring Station, 6 stations (Station Operator: JWA) |
Primary Station: Matsushiro (PS22) Sending seismic data to the IDC 24 hours on-line. |
Auxiliary Station: Ohita (AS51), Kunigami (AS52), Hachijojima (AS53), Kamikawa-asahi (AS54), Chichijima (AS55) Sending seismic data on the request of the IDC. |
|---|---|
| Infrasound Monitoring Station, 1 station (Station Operator: JWA) | Isumi (IS30) Sending infrasound data to the IDC 24 hours on-line. |
| Radionuclide Monitoring Facilities, 3 stations (Station Operator: JAEA) | Radionuclide Monitoring Station: Okinawa (RN 37), Takasaki (RN38) |
| Radionuclide Laboratory: Tokai (RL11) |
JWA: Japan Weather Association, JAEA: Japan Atomic Energy Agency
Map of Monitoring Facilities in Japan
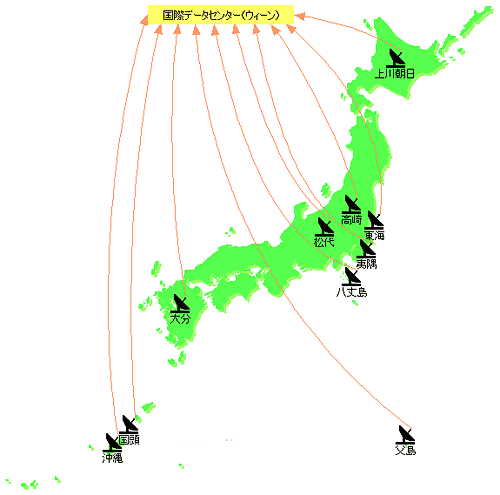
These 10 stations collect data and send them to the IDC in Vienna, where the CTBTO Preparatory Commission is located. The IDC handles/stores the data and provides relevant data as well as Revised Event Bulletin created by the IDC. Each signatory has to analyze/evaluate these data, to identify the phenomenon caused by nuclear test explosions and to determine the necessity of on-site inspection.


